THE CONSTELLATIONS AND GREEK MYTHOLOGY
|
Greek mythology and the Constellation Cygnus
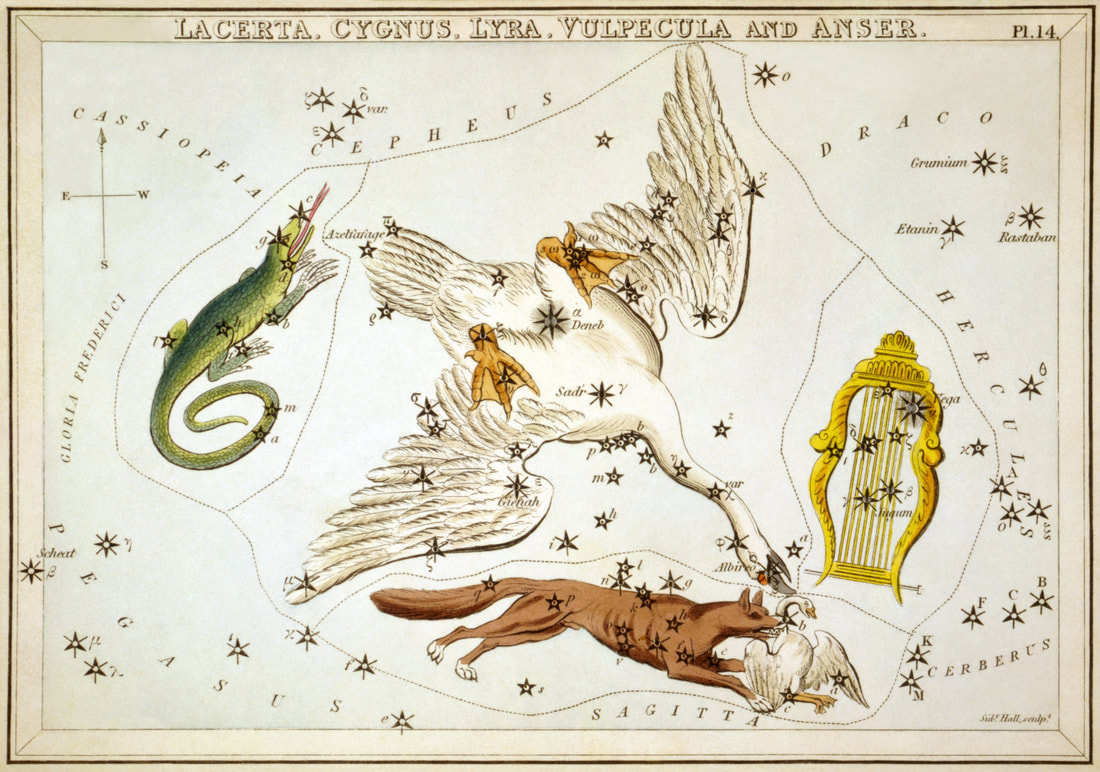
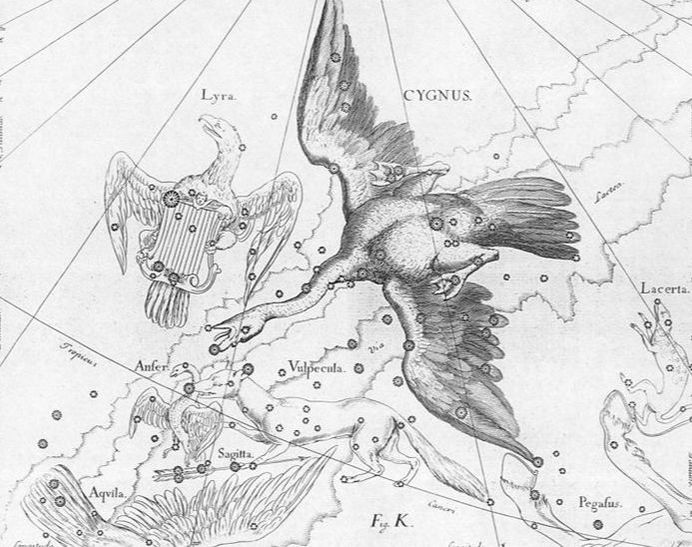
The constellation Cygnus was, according to the Ancient Greeks, a representation of the Swan, a bird which appeared in Greek mythology almost as often as the eagle.
It is most commonly said that the Swan depicted by the Cygnus constellation is that of Zeus who had disguised himself as the bird in order that he might seduce the beautiful Leda, wife of King Tyndareus of Sparta. Zeus was successful in his seduction of Leda, who subsequently gave birth to Helen and Pollox (Polydeuces), as children of Zeus, as well as Clytemnestra and Castor, as children of Tyndareus. |
Zeus subsequently placed the likeness of the swan amongst the stars as Cycnus is recognition of his conquest.
The names Cygnus and Cycnus was common in Greek mythology and occasionally the constellation is said to be a representation of Cycnus, son of Ares, who was killed by Heracles, of Cycnus, son of Poseidon, who was killed by Achilles, or Cycnus, a friend of Phaethon, who mourned the death of the son of Helios.
The names Cygnus and Cycnus was common in Greek mythology and occasionally the constellation is said to be a representation of Cycnus, son of Ares, who was killed by Heracles, of Cycnus, son of Poseidon, who was killed by Achilles, or Cycnus, a friend of Phaethon, who mourned the death of the son of Helios.
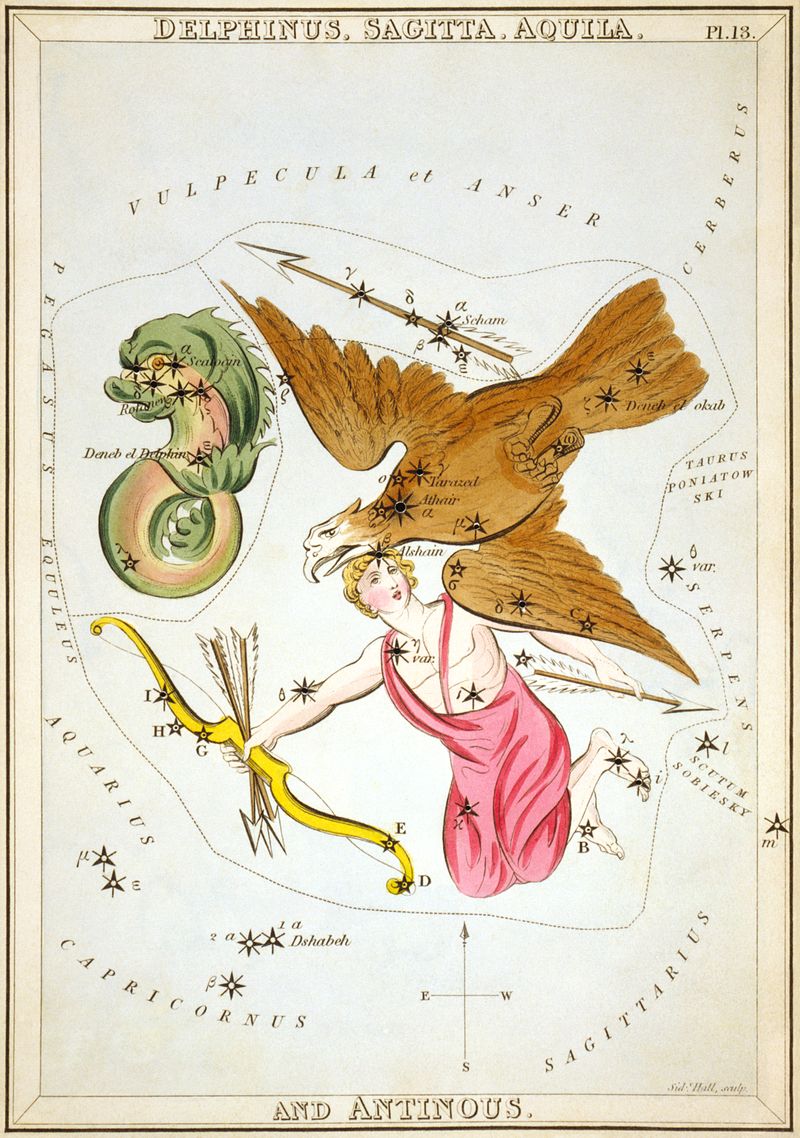
Greek mythology and the Constellation Delphinus
|
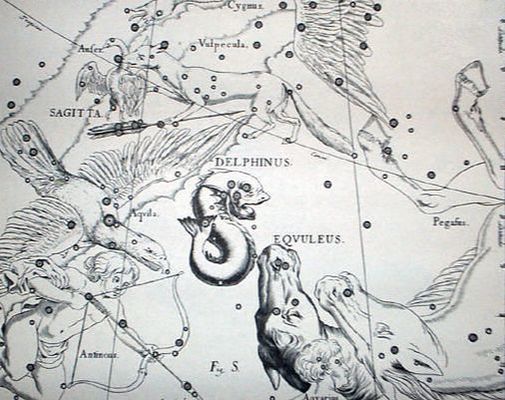
Dephinus, the Dolphin, is one of Ptolemy’s 48 constellations, and its story is most commonly associated with the sea god Poseidon.
In Greek mythology, Poseidon had decided that the Nereid Amphitrite was to be his bride, but Amphitrite was reluctant to marry the Olympian god. As a result, Amphitrite would hide herself away, avoiding those messengers of Poseidon sent to find her; eventually though, Delphin, a minor sea god, whose appearance was that of a dolphin, found her. Delphin was eloquent enough to persuade Amphitrite to agree to marry Poseidon. Poseidon was so grateful for the efforts of Delphin that he placed the likeness of the sea god amongst the stars so that he would always be remembered. |
Occasionally it was said that Delphinus was actually the representation of the dolphin which saved the poet Arion from drowning, or one of the Tyrrhenian pirates who had been transformed by Dionysus into dolphins when they had the affront to capture the god.
|
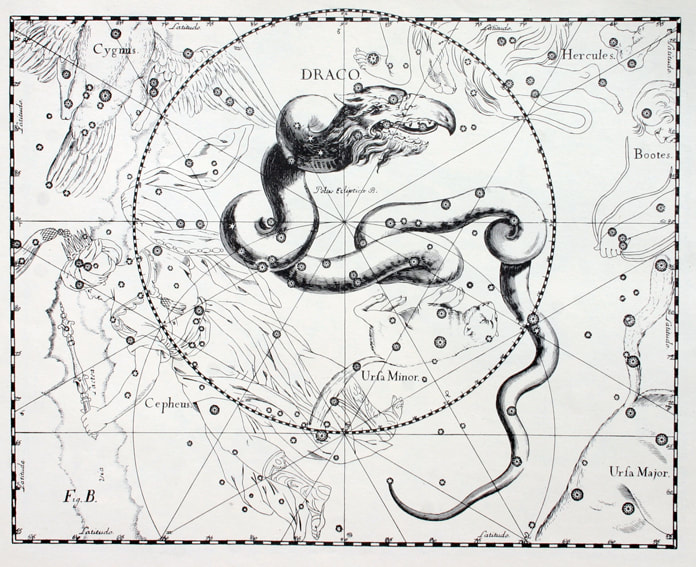
Greek mythology and the Constellation Draco
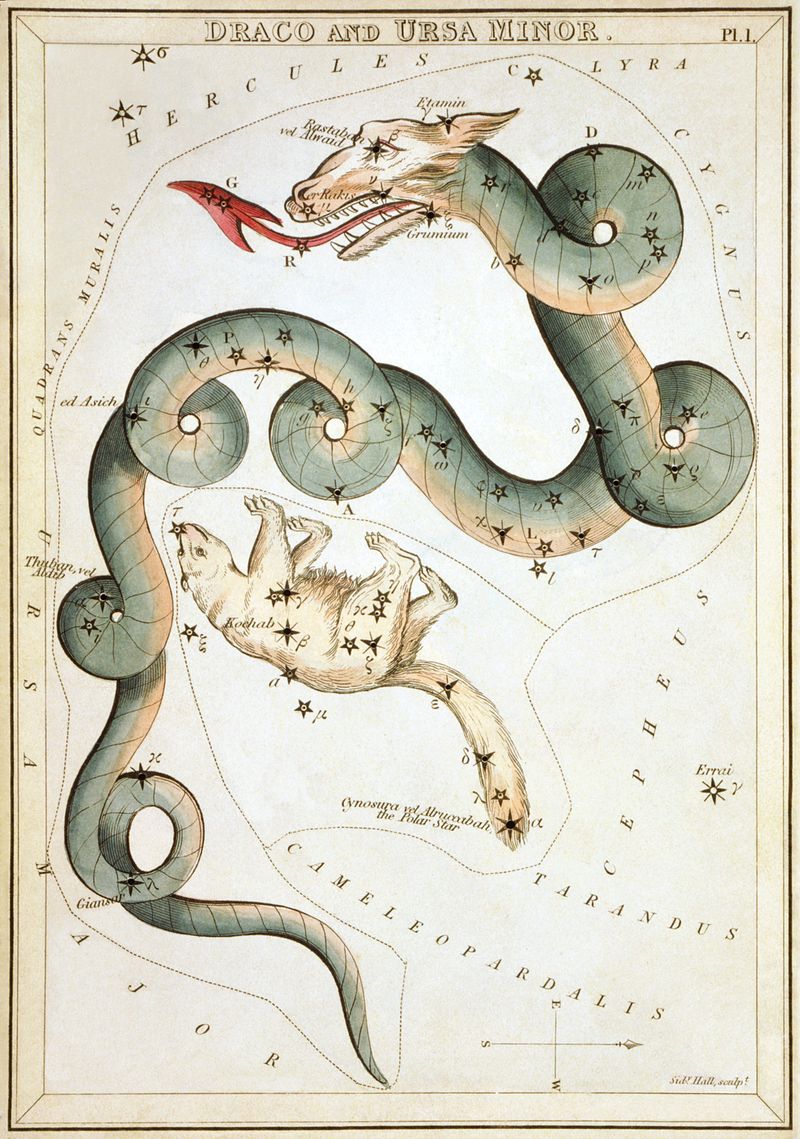
The constellation Draco is said to be the representation of a Dragon from Greek mythology.
The idea of dragons and gigantic serpents were common features of Greek mythological tales, with the name dragon or serpent being used interchangeably. The constellation Draco is most commonly said to represent Ladon, the dragon found in the Garden of Hera alongside the Hesperides. Ladon would guard the legendary Golden Apples found inside the Garden of Hera, but when Heracles had need of them for one of his labours, the Greek hero killed Ladon. It is also said by some that it was Atlas who killed Ladon, rather than Heracles, for Heracles was holding up the heavens whilst Atlas retrieved the Golden Apples. |
Less commonly, the constellation Draco is named as the dragon made use of by the Gigantes during the Gigantomachy. This dragon was thrown at Athena during the war, but the goddess caught hold of it and threw it into the heavens.
There were other dragons spoken of in Greek mythology, including Kampe, the guard of Tartarus, the dragon of Ares slain by Cadmus, and Typhon, the monstrous beast who challenged the rule of Zeus.
There were other dragons spoken of in Greek mythology, including Kampe, the guard of Tartarus, the dragon of Ares slain by Cadmus, and Typhon, the monstrous beast who challenged the rule of Zeus.
|
Greek mythology and the Constellation Equuleus
The constellation Equuleus is one of the least defined in Greek mythology, although it of course represents a small horse.
One possibly source of the constellation Equuleus in Greek mythology is the tale of Melanippe (also known as Hippe), daughter of the centaur Chiron. Melanippe was courted by Aeolus, son of Hellen, and Melanippe fell pregnant. Wishing to hide her pregnancy from her father, Melanippe hid upon Mount Pelion, but when her father came looking for her, Melanippe prayed to Artemis for help, and the goddess transformed her into a mare. Whilst in horse form, Melanippe gave birth to a daughter, Arne, who though born in foal form, was later transformed into human form. It was Artemis who later put Melanippe’s likeness into the stars, although as she is still hiding from Chiron, the constellation Centaurus, only her head is visible. Some say though that the constellation Equuleus is a different horse, potentially Celeris, the offspring of Pegasus, and the swift horse who was later owned by Castor. |
|