THE CONSTELLATIONS AND GREEK MYTHOLOGY
|
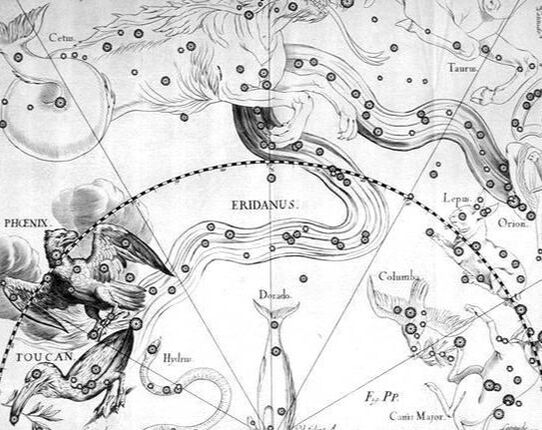
Greek mythology and the Constellation Eridanus
The constellation Eridanus, in Greek mythology, is the representation of a great river, a river normally said to be the Eridanus, but also named by others as the River Nile.
In the case of the constellation Eridanus being named for a river of the same name, then a look on a current map will fail to produce said river, for in Greek mythology, the Eridanus was a river believed to run through the mythical land of Hyperborea; the land beyond the North Wind. The name Eridanus is normally translated as “early burnt”, and as a result the earthly river is associated with the story of Phaethon. Phaethon was said to have fallen into the river after Zeus had knocked him from the sun chariot with a thunderbolt. Subsequently, the Eridanus River was equated with both the Po and Danube. |
|
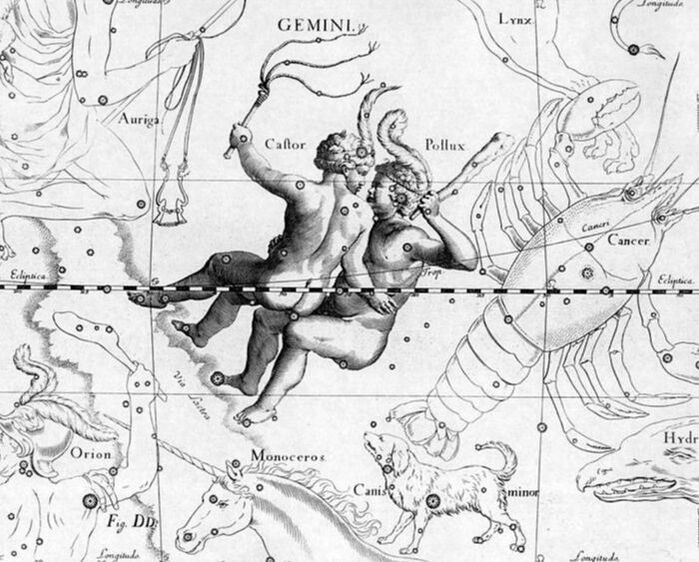
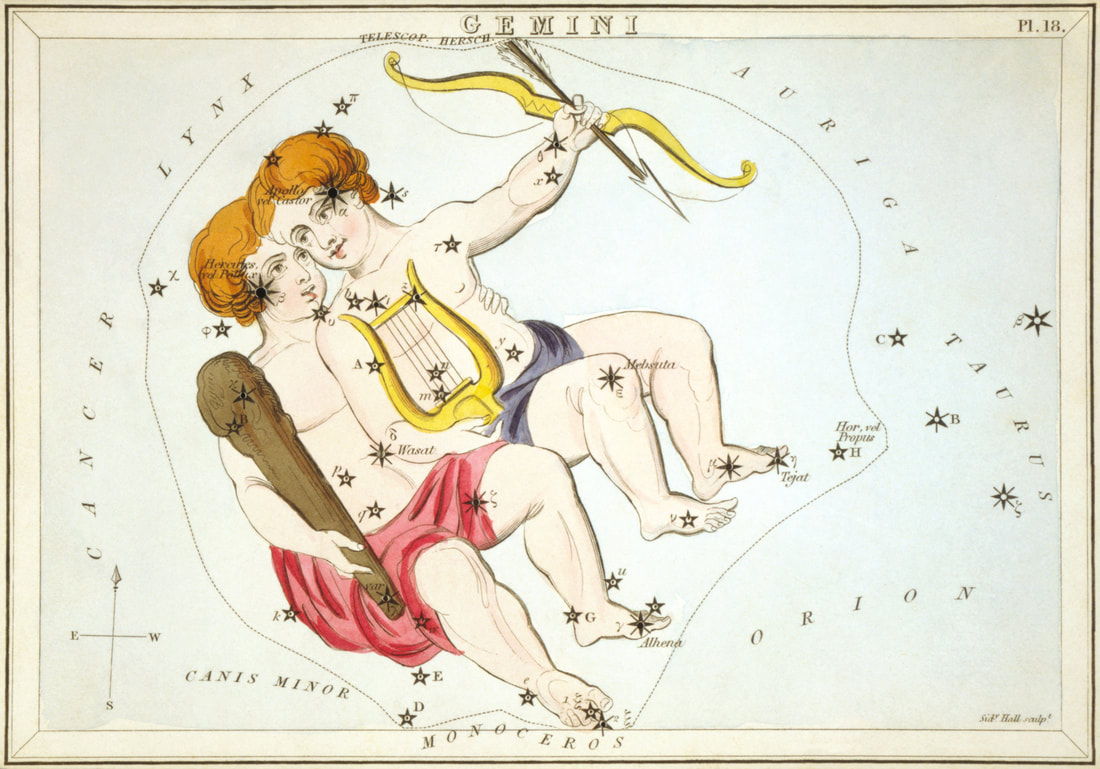
Greek mythology and the Constellation Gemini
|
Gemini is one of the most famous of constellations, being also a sign of the zodiac. Gemini of course represents the “Twins”, who were most commonly named as Castor and Pollox (Castor and Polydeuces), the Dioscuri, from Greek mythology.
Castor and Pollox were twin sons of Leda, the Spartan Queen, but whilst Castor was the mortal son of Leda’s husband, Tyndareus, Pollox was the immortal son of Zeus. Noted heroes in Greek mythology, Castor and Pollox would rescue their sister Helen when she was abducted by Theseus, and would also become Argonauts. When however Castor was killed, Pollox decided to give up his own immortality, and thus the two brothers were placed amongst the stars by Zeus. Whilst the constellation Gemini is most commonly said to represent Castor and Pollox, it was also said by some that the pair of figures were actually Apollo and Heracles, who famously wrestled when Apollo angered Heracles. |
|
|
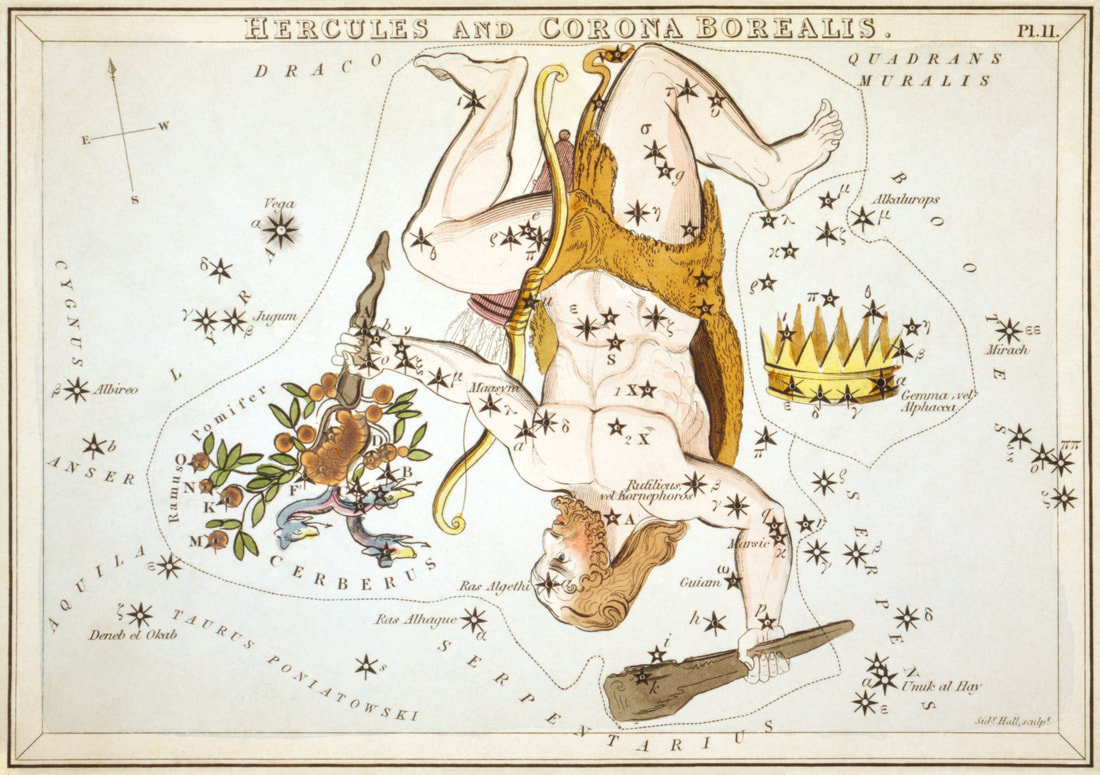
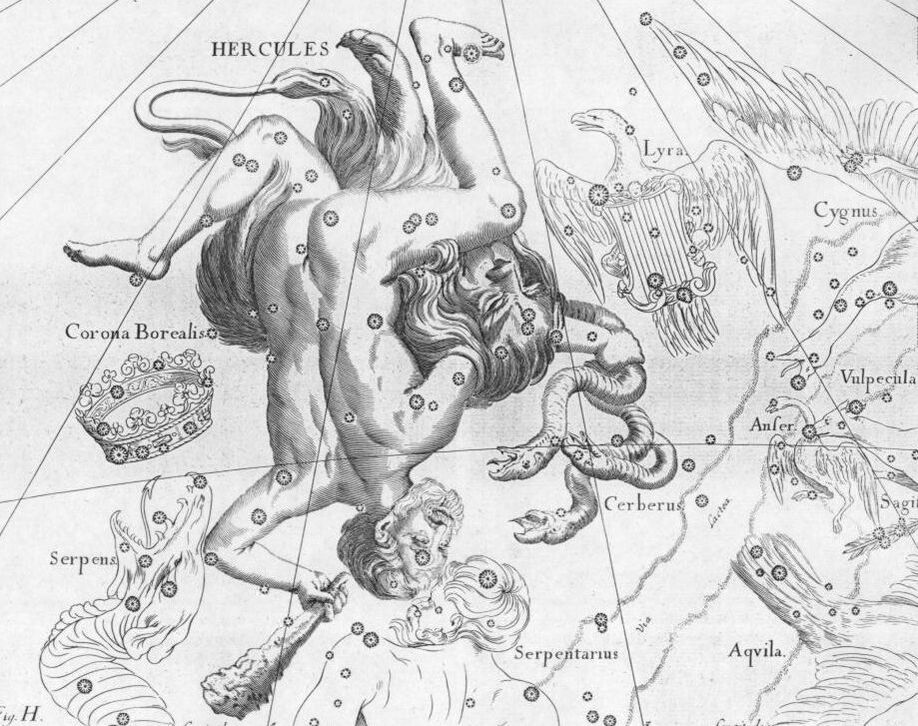
Greek mythology and the Constellation Hercules
The constellation Hercules is named for the greatest of Greek heroes, Heracles. The demi-god son of Zeus and Alcmene was known for his many adventures fighting giants, monsters and men.
The Greeks called the constellation “Engonasin” the kneeler, and was generally considered to be Heracles in a kneeling position. Two different versions are given as to why Heracles is thus depicted as kneeling, either he was kneeling as he was about to give the killing blow to Ladon, the dragon-guard of the Garden of the Hesperides, or else Heracles was kneeling in exhaustion after he battled with the Ligurians. Despite the name of the constellation the kneeling figure amongst the stars is not always said to represent Heracles for it was also said by some to represent Theseus, who was kneeling to retrieve his father’s weapons from beneath a boulder; Ixion, who was being punished by being bound to a fiery wheel in the heavens; or it was Orpheus, who was kneeling next to his lyre (the constellation Lyra). |
|
|
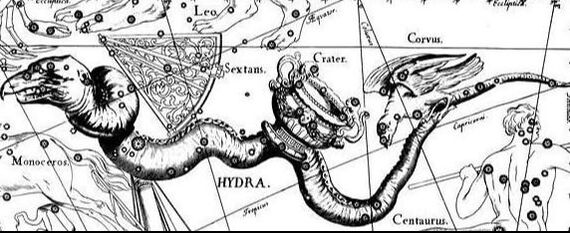
Greek mythology and the Constellation Hydra
Hydra is the Water Serpent constellation and is most commonly said to represent the Lernaean Hydra from Greek mythology; the Lernaean Hydra being one of the monstrous offspring of Echidna.
The Lernaean Hydra was a multi-headed water serpent who lived in the marshes of Lerna. Heracles was tasked by Eurystheus, at Hera’s bidding, to kill the Lernaean Hydra for one of his Labours. The antipathy of Hera towards Heracles was such that she was attempting to kill her husband’s son. Aided by Iolaus, Heracles was soon getting the better of the Lernaean Hydra, and so Hera sent Carcinus (Cancer) to aid the Water Serpent, but to no avail, and as both the Lernaean Hydra and Carcinus were killed, Hera placed the likeness of both amongst the stars in recognition of their efforts. |
|
A less common Greek myth has the Hydra actually represent a water serpent of Apollo, whom the god placed in the stars to prevent Corvus (the crow) from drinking of Crater (the bowl).