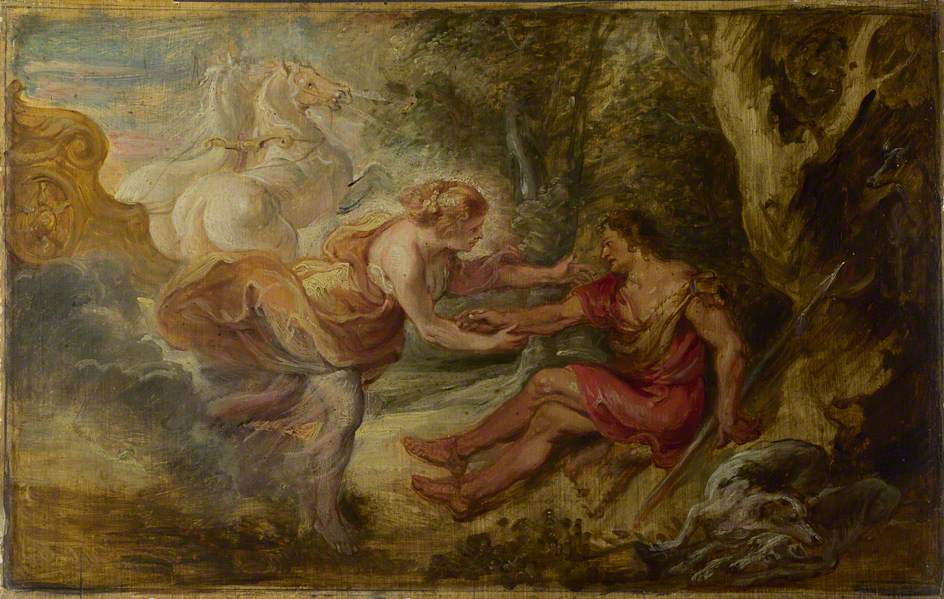STORY OF CEPHALUS IN GREEK MYTHOLOGY
Cephalus of Phocis
Cephalus of Phocis was a mortal prince in Greek mythology, famous for being the husband of Procris, the Athenian princess. At one time Cephalus was the owner of the legendary hunting dog Laelaps, and also a comrade of the Theban general Amphitryon.
Cephalus Son of DeioneusCephalus was a son of Deioneus, the king of Phocis, and his wife Diomede. Thus Cephalus was sibling to Actor, Aenetus, Asterodia and Phylacus.
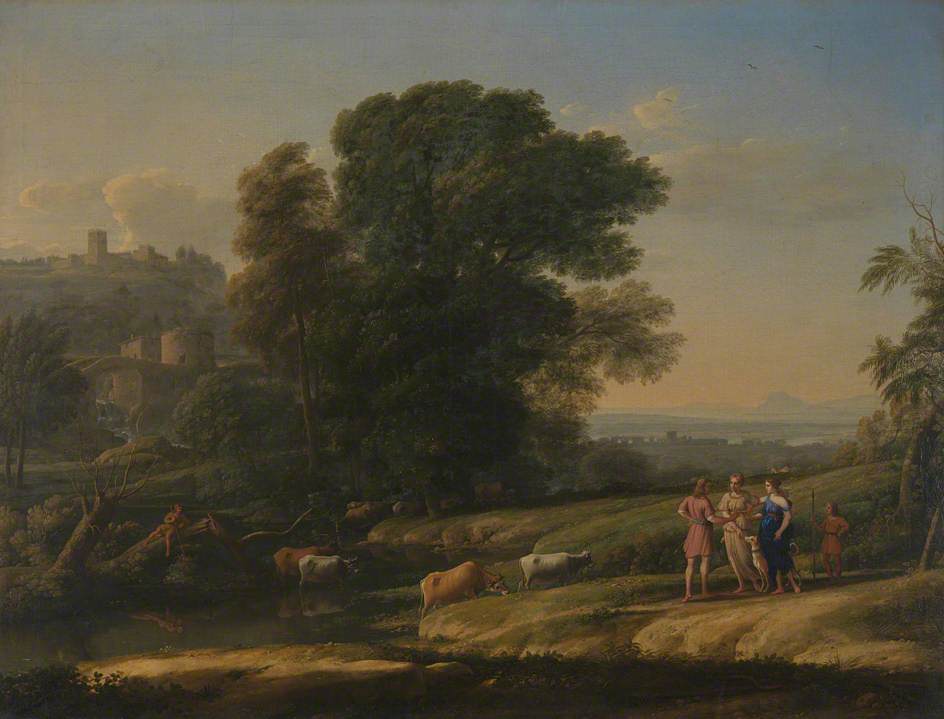
Cephalus would travel from Phocis to Athens were he fell in love with Procris, the daughter of the king of Athens, Erechtheus. |
|
Cephalus and Eos
The love of Cephalus and Procris would be tested, and husband and wife would be forced apart. Some tell of Cephalus simply leaving his wife, in order that he could test her fidelity; whilst other ancient sources tell of the goddess Eos abducting Cephalus, for the goddess of the Dawn had herself fallen in love with Cephalus.
Cephalus would become a lover of Eos, and the goddess might have born several children for the prince, including Phaethon, Tothonos and Hesperus. In Greek mythology though, Eos was also said to have another Cephalus, the son of Hermes and Herse, who is also named as father of the aforementioned children.
Cephalus would become a lover of Eos, and the goddess might have born several children for the prince, including Phaethon, Tothonos and Hesperus. In Greek mythology though, Eos was also said to have another Cephalus, the son of Hermes and Herse, who is also named as father of the aforementioned children.
Cephalus Tests Procris
|
Even though in the company of a goddess, Cephalus would long to return to his wife, and Eos, annoyed at being second best to a mortal, would attempt to show how unfaithful Procris was. Cephalus would thus be returned to Athens in a disguised form, and simply by offering money to Procris it was said that Procris would commit adultery.
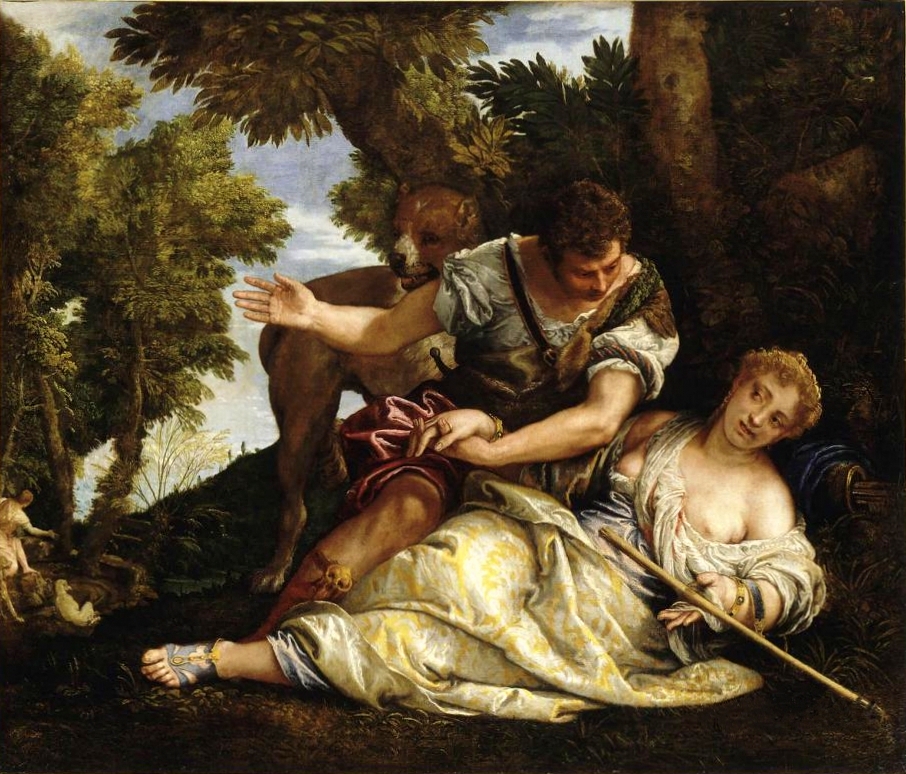
Other say that Cephalus instead asked Pteleon to test his wife’s fidelity, and Procris decided to cheat on Cephalus after being bribed with a golden crown. Procris Tests cephalusWhen Procris realised that she had been discovered as an adulteress, she fled from Athens, and eventually ended up on Crete, but she would return to Athens with Laelaps, the hunting dog, and a javelin that always hit its mark.
Cephalus was then tested by his wife, for she returned in disguise as a youthful hunter, and whilst Cephalus wished to buy Laelaps and the javelin, the disguised Procris would only give up the gifts if Cephalus agreed to sleep with him/her. When Cephalus agreed, he too was revealed as a cheater, and so husband and wife would be reconciled; and Procris would give the gifts to Cephalus. Cephalus was said to have become father of Arcesius by Procris, who in turn became father of Laertes, who was father of Odysseus, who was father of Telemachus. |
|
Cephalus and the Death of ProcrisThere remained a level of mistrust between husband and wife though, and when Procris heard a rumour that Cephalus was again cheating on her, she followed her husband and spied on him from a thicket.
Cephalus would call out for Aura (or Zephyr or Nephele) to come to him, but it was an innocent request for he was simply asking for a cooling breeze, but an agitated Procris at that moment made a rustling sound in the thicket. Cephalus, believing that the noise was from a wild animal, threw his newly acquired javelin at the thicket, and as was its want, the javelin hit its mark. Cephalus had killed his wife, but Procris would die happily in his arms, when Cephalus explained that he was not cheating on her. It was said that Cephalus was subsequently tried upon the Areopagus (Ares Rock), although this was a place normally associated with trials of deliberate murder rather than accidental death. Nevertheless, for causing the death of Procris, Cephalus was banished from the city of Athens. |
|
Cephalus in Exile
In exile, Cephalus was found by Amphitryon who was in need of the services of Laelaps. Amphitryon needed the army of Creon of Thebes in order to go to war with the Teleboans, but Creon had set a condition that Amphitryon must rid Thebes of the Teumessian Fox, hence the need for Laelaps.
Cephalus would agree to the loan, although he never got Laelaps back, as long as he could go to war with Amphitryon against the Teleboans.
So Cephalus and his small band of soldiers joined the forces of Amphitryon and Creon in a war against the kingdom of Taphos. Amphitryon did win the war, and as a reward Cephalus was given the island of Same in the Ionian Sea.
Same would subsequently be renamed Caphallenia after its new ruler, and Cephalus would marry Clymene, daughter of Minyas. Some sources would claim that it was Clymene, rather than Procris, who bore Cephalus Arcesius.
Ancient sources do state that Clymene did bear Cephalus four sons, Crane, Pali, Pronnoi and Same, who would found the four main cities of ancient Cephallenia.
A few of these same ancient sources also tell of the death of Cephalus, for he was not destined to live into old age, and still remorseful about the killing of his first wife, Cephalus was said to have leapt to his death from the clifftops, possibly at Cape Leucas.
Cephalus would agree to the loan, although he never got Laelaps back, as long as he could go to war with Amphitryon against the Teleboans.
So Cephalus and his small band of soldiers joined the forces of Amphitryon and Creon in a war against the kingdom of Taphos. Amphitryon did win the war, and as a reward Cephalus was given the island of Same in the Ionian Sea.
Same would subsequently be renamed Caphallenia after its new ruler, and Cephalus would marry Clymene, daughter of Minyas. Some sources would claim that it was Clymene, rather than Procris, who bore Cephalus Arcesius.
Ancient sources do state that Clymene did bear Cephalus four sons, Crane, Pali, Pronnoi and Same, who would found the four main cities of ancient Cephallenia.
A few of these same ancient sources also tell of the death of Cephalus, for he was not destined to live into old age, and still remorseful about the killing of his first wife, Cephalus was said to have leapt to his death from the clifftops, possibly at Cape Leucas.